How to Use Google Search Console in 2024
Google Search Console is a free tool from Google designed to help people improve their website’s SEO and monitor its performance. It’s one of the most crucial resources you can have for making sure your website is performing well on Google, but its also not the easiest tool out there to use and understand. So let’s look closer at Google Search Console and show you how to use it and why its important in the first place.
What is Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a resource that will let you understand how the search engine views your website and how you can help Google see it more favorably. Google Search Console tracks and shares a lot of information that we’ll look at later, but primarily, it’s a way for users to keep tabs on how many people have found their website on Google and how often those impressions lead to actual website visitors.
Google Search Console also lets you see which of your pages are actually showing up on Google and which ones aren’t. You don’t need Google Search Console to show up on Google, but at the same time, neither you nor Google are infallible. Your pages might not be showing up on Google at all for one reason or another, whether because of something you did or something Google did. And having a Google Search Console page will let you know when that’s happening, while you wouldn’t be able to tell for sure which pages are showing up without Search Console.
How You Can Use Search Console To Your Advantage
Google Search Console is a way to keep tabs on every element of your website, primarily your pages’ performance. You can use this information to see which pages are underperforming and audit their SEO to find out what’s wrong and how you can drive more traffic there, potentially using your well-performing pages as a reference for how to build the rest of your website.
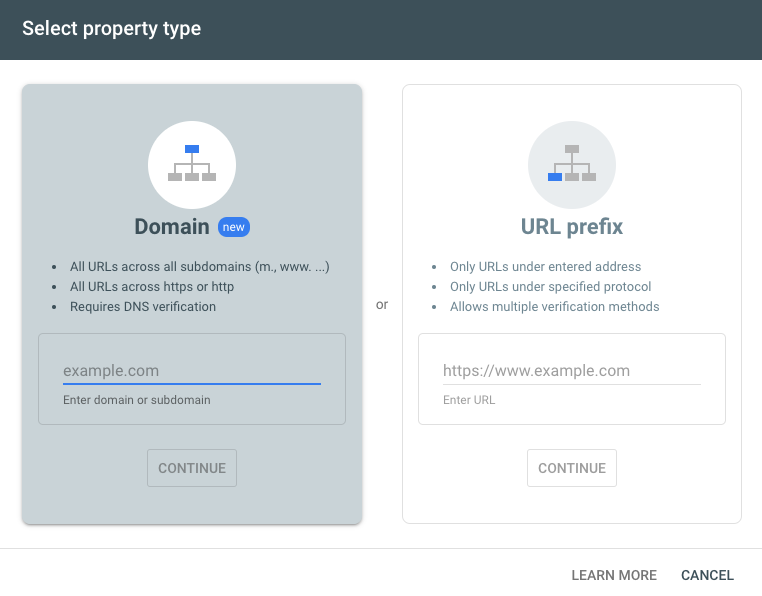
How to Set Up Your Website on Google Search Console
Google Search Console’s two options for linking a URL to the platform.
As you can see, Google Search Console is a resource with several benefits. But to reap those rewards, you have to first climb the hurdle of getting your website set up on the Search Console - which can be tricky if it's your first time.
Using a Domain Property For a Squarespace Website
The best way to set up your website on Google Search Console is to use a domain property. And though this method is a bit more complex than using a URL prefix, the first step is pretty straightforward - simply enter your website domain into the property field. After that, Google will request that you verify your ownership over the domain, which, if you’re on Squarespace, you can do with the following steps:
Copy the auto-generated text record from Google Search Console and log into your Squarespace account.
From the backend of the website you wish to link to Google Search Console, click on the Settings tab, then Domains & Email and select the domains option, select the domain you entered in the first step of the process, and hit the DNS records button on the right-hand side of the screen.
Go to the Custom Records section and hit the “Add Record” button. From there, enter the ‘@’ symbol in the host field, select ‘TXT’ for the record type, and paste the text record from Google into the data field. You can leave the priority field blank.
Submit the finalized text record and return to Google Search Console to verify your ownership.
Google Search Console First Steps
It takes Google a day or two to process all the information from your website, so you won’t get any updates on your page traffic immediately. But eventually, Google Search Console will be able to track how many visitors your website and all its individual pages get, and from there, you can start using the resource to improve your website’s reach. But first, you need to give Google a way to actually track all the traffic data.
The quickest way to point Google in the direction of the pages you want to monitor is to submit a sitemap of your website. Sitemaps are essentially lists of all the pages and content on your website, and you can submit one to Google Search Console so that the search engine knows exactly what pages you want it to index.
To submit a sitemap, go to the sitemaps section on Google Search Console, enter your website’s full URL, and add /sitemap.xml at the end of it.
Adding Users
If you want more than one person to be able to view the data on Google Search Console, you can add additional users with varying levels of permissions after setting up your page. To do this, select the “Settings” tab from the menu on the left-hand side, click on “Users and Permissions,” and hit the blue “Add User” button from there. After that, enter the email address of the new user and assign them one of three available roles: Restricted, Full, and Owner.
Restricted users can view some of the data available in Google Search Console but can’t edit any settings or information.
Full users can view all the data available in Google Search Console but can only make a handful of changes to the settings.
Owners have full access to all the data and settings in Google Search Console.
Google Search Console’s Most Important Data Points
Google Search Console’s home page.
Clicks and Impressions
Clicks and impressions are the two fundamental elements of Google Search Console’s data tracking. Impressions are simply how many times your website appears in search results, regardless of whether or not it leads to someone visiting your website. Clicks are when your website shows up in search results and someone clicks on the result, taking them to the page.
Impressions are a great way to track how well your website is optimized for search engines. If your pages are creating a lot of impressions, it means that you’ve done a good job building your content in a way that's easy for search engines to find and recommend. If your pages are generating a lot of clicks, it means that you’ve done a good job putting them in front of the people that need them.
The combination of clicks and impressions your website gets is called “click-through rate (CTR).” CTR is a percentage of how many people see your website (impressions) and actually click on it (clicks). For example, if your website makes 100 impressions and two people click on it, you would have a CTR of 2% since 2% of the people who saw your website as a Google search result interacted with it.
Average Position
The average position stat measures where your website ranks on average when it appears in search results. If Google Search Console displays that you have an average position of 1.5, it means your website is usually the first or second result whenever it does rank - which should be the loftiest goal for every website. On the other hand, if your average position is in the 40s or 50s, it means that you’re ranking outside the first couple of pages of search results and likely need to change up your content to rank better.
You can use the average position stats as a barometer of how well your pages are ranking for your current SEO keywords and modify your approach based on the performance.
Links Data
Google Search Console’s links tab tracks how often other websites link to your website or web pages (this process is known as backlinking). In addition to seeing how many total times external websites have linked to yours, you can use this tab to track what pages they are linking to and how often they’re linking to them, the websites that link to yours the most, and the anchor text they’re using in the backlinks (a selection of text in a blog with an external link is an example of anchor text).
A Beginner’s Guide to Page Indexing
When a page from your website is indexed, it means that Google has analyzed it and all of its content and has stored it in its database. And when your content is in Google’s database, the search engine can recommend it whenever someone makes a relevant search inquiry. On the other hand, if your pages aren’t indexing for whatever reason (and there are many reasons), Google won’t be able to store them in its database or recommend them in any search results.
If you are experiencing indexing problems, the first thing you should do is request a manual index from Google with these steps:
On the left-hand side menu, scroll down to and click on the section titled 'Pages' in the indexing drop-down menu.
Scroll down to the menu titled "Why Pages Aren't Indexed" and click on one of the reasons listed.
After clicking on one of the problem areas, scroll to the bottom of the page and click on one of the non-indexed URLs. Doing this will pull up a menu on the right side of your screen with an option to inspect the URL. Click on the option and it will take you to a new page.
On the new page, there will be a button on the right-hand side of the screen with the option to 'Test Live URL' - this will let you see if the URL is live and working. Click on it, and if the page updates saying that the "URL is available to Google," it's a great sign that the manual index will work. After that, hit the "request indexing" button, and it will make the search engine look for that page again to store it in the index.
In some cases, Google might not index your page even if it should technically be able to. In many of those instances, the manual indexing should fix whatever issues Google Search Console was experiencing. Of course, some error messages are the result of deeper problems. For a closer look at how to resolve some of those, read through our blog on resolving some of the more common error messages Google Search Console users receive here.
Those are some of the basics we feel you should know about Google Search Console, but theres a lot more you can do with the resource (and more the resource can do for you) than what we’ve discussed. So dive into Google Search Console and see for yourself how helpful this free tool can be!
Need help with SEO? Book a consultation and learn more about how we can help!